Erythritol has become a widely used sugar substitute due to its low-calorie content and natural origin. Found naturally in some fruits and fermented foods, erythritol belongs to the sugar alcohol family, offering a sweet taste with none of the calories or blood sugar spikes associated with regular sugar. In this article, we will explore erythritol’s background, its sweetening properties, and the health benefits it provides.
What is Erythritol?
Erythritol is a type of sugar alcohol, a carbohydrate that occurs naturally in some foods. It is about 60-70% as sweet as sugar but contains virtually no calories, making it an attractive option for those looking to reduce their calorie intake while still enjoying sweetness.
Origins and History
Although erythritol occurs naturally in fruits like watermelon, pears, and grapes, it is typically produced through the fermentation of glucose. The process of extracting erythritol involves breaking down starches, such as corn or wheat, into glucose, which is then fermented to create the sweetener.
- First discovered in 1848 by British chemist John Stenhouse.
- Commercially used in Japan since the early 1990s as a sugar substitute.
- Now widely available in various forms around the world.
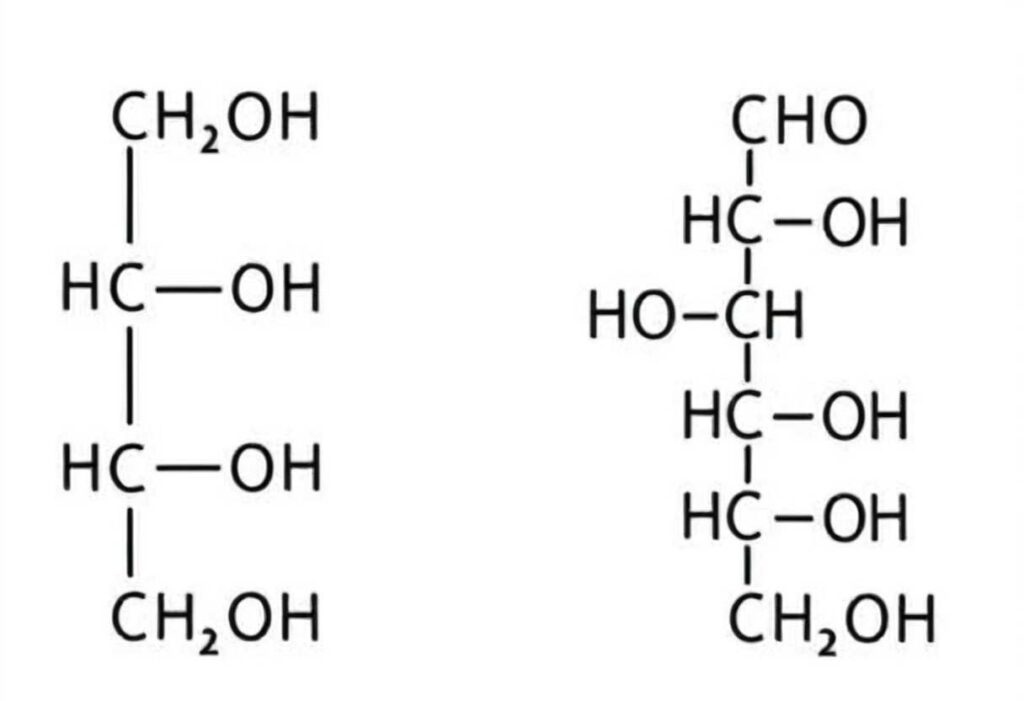
How Erythritol is Made
To produce erythritol commercially, manufacturers often rely on fermentation processes. Typically, glucose from corn or wheat is fermented with a natural yeast, resulting in erythritol crystals that can be used as a sweetener. After fermentation, the product is purified and crystallized to create a powder or granule format that is ready for use in foods and beverages.
Erythritol as a Sweetener
Erythritol’s unique properties make it a popular choice as a sugar alternative. It provides sweetness without the calories or impact on blood sugar, making it ideal for individuals on low-carb diets or managing diabetes.
Sweetness Level
Erythritol is not as sweet as regular sugar, with a sweetness level of about 60-70% compared to sucrose. Despite this, it blends well with other sweeteners and offers a clean, sugar-like taste without bitterness. Many people combine erythritol with other sugar substitutes, like stevia or monk fruit, to enhance its sweetness.
- Erythritol is about 60-70% as sweet as sugar.
- It can be combined with other sweeteners for a more balanced taste.

Health Benefits of Erythritol
In addition to providing sweetness without the calories, erythritol offers several health benefits. It’s an excellent choice for people seeking to control their blood sugar or reduce their calorie intake.
Calorie-Free Sweetness
Unlike sugar, which adds empty calories to your diet, erythritol passes through the body without being metabolized. This means it doesn’t contribute to weight gain and can be an effective tool for managing or losing weight.
- Contains only 0.24 calories per gram, compared to sugar’s 4 calories per gram.
- Does not affect cholesterol or triglyceride levels, making it a heart-healthy alternative.
Ideal for Blood Sugar Control
Erythritol has a glycemic index of zero, meaning it doesn’t raise blood sugar or insulin levels. This makes it an ideal sweetener for diabetics and individuals following a low-carb or ketogenic diet.
- Does not impact blood sugar levels.
- Safe for diabetics and those managing insulin resistance.
Dental Health Benefits
Unlike sugar, erythritol does not contribute to tooth decay. In fact, studies suggest that it may help prevent cavities by inhibiting the growth of bacteria that cause dental plaque. This makes erythritol a tooth-friendly alternative to sugar and other sweeteners.
- Does not cause tooth decay.
- May help reduce dental plaque and improve oral health.
Erythritol vs. Other Sweeteners
With so many sugar alternatives on the market, it can be challenging to choose the best option. Understanding how erythritol compares to other sweeteners can help you make an informed decision.
Erythritol vs. Stevia
Both erythritol and stevia are popular natural sweeteners, but they differ in several key ways:
- Taste: Erythritol has a neutral, clean taste, while stevia can sometimes leave a bitter aftertaste, which may affect the flavor of food or drinks.
- Use in Recipes: Erythritol is often combined with stevia to improve sweetness without altering taste, making it a versatile choice in recipes where you want a sugar-like flavor.
Erythritol vs. Sugar
When compared to sugar, erythritol offers many advantages, particularly for those looking to reduce calorie intake or manage blood sugar levels.
- Caloric Content: Sugar is high in calories and contributes to weight gain, while erythritol provides sweetness with virtually no calories.
- Blood Sugar Impact: Sugar causes spikes in blood sugar and insulin levels, while erythritol does not affect blood glucose levels, making it a better choice for diabetics.
Potential Side Effects and Safety Concerns of Erythritol

Erythritol is safe for most people, but overconsumption may cause mild side effects in some cases.
Digestive Discomfort
Some people experience bloating or gas when they consume too much erythritol. While small amounts are typically fine, larger quantities may lead to discomfort.
- Easy on Digestion: Erythritol passes through the body quickly, reducing the risk of digestive issues.
- Consume in Moderation: Consuming more than 50 grams daily can increase the chance of bloating or discomfort, especially for individuals sensitive to sugar alcohols.
Allergic Reactions
Though uncommon, allergic reactions may occur. Symptoms like itching or rashes can indicate an allergy. If you notice these symptoms, it’s important to stop using erythritol and consult a doctor.
- Rare Cases: Allergies to erythritol are rare, but monitoring for any signs is important, especially when trying it for the first time.
Is Erythritol Safe for Children and Pregnant Women?
Children and pregnant women can safely consume erythritol in moderate amounts. Introducing small portions initially helps prevent potential digestive discomfort, especially in young children.
- Safe for All: Approved by food safety authorities, erythritol can be consumed by all age groups, including children and pregnant women.
Erythritol in Cooking and Baking
Erythritol serves as a great substitute for sugar in many recipes. It sweetens dishes without the calories or impact on blood sugar that sugar has, though slight adjustments might be needed for texture and moisture.
Baking with Erythritol
You can replace sugar with erythritol in most baked goods using a 1:1 ratio. It doesn’t caramelize or hold moisture like sugar, so minor adjustments in your recipe may be necessary.
- Best for Keto Baking: Erythritol is popular in low-carb and keto baking since it sweetens without increasing blood sugar.
- Adjustments Needed: Baked goods may come out drier, so modifying the recipe can improve texture.
Erythritol in Drinks
Erythritol dissolves well in both hot and cold drinks. It’s perfect for sweetening coffee, tea, or lemonade without leaving an aftertaste, which some artificial sweeteners tend to do.
- Perfect for Beverages: Erythritol enhances drinks, keeping their original flavor intact, making it ideal for people seeking a sugar-free option.
Cooking with Erythritol
Erythritol works well in a variety of savory dishes, sweetening sauces, dressings, or marinades. It adds sweetness without adding calories or affecting blood sugar levels.
- Versatile for Cooking: You can use erythritol to sweeten sauces and salad dressings without impacting the flavors of your dish.
Erythritol in Commercial Food Products
Erythritol is a common ingredient in many sugar-free and low-calorie products. It provides sweetness without sugar’s harmful effects, making it popular in food products marketed for those reducing their sugar intake.
Common Products with Erythritol
Many popular brands use erythritol in a variety of products, including:
- Sugar-Free Candies and Chocolates: Erythritol is often used in sugar-free candies and chocolates to provide sweetness without raising blood sugar.
- Low-Calorie Ice Cream: Numerous low-calorie ice cream brands use erythritol as a sweetener to reduce sugar and calories.
- Sugar-Free Beverages: It is widely used in sugar-free sodas and flavored waters, offering sweetness without adding any calories.
Erythritol’s neutral taste and zero impact on blood sugar make it an excellent choice for health-conscious consumers.
Erythritol vs. Other Sweeteners
Here’s how erythritol compares to other sweeteners like stevia, xylitol, and traditional sugar.
Erythritol vs. Xylitol
Both erythritol and xylitol are sugar alcohols, but they have some differences in their use and effects.
- Calories: Xylitol has more calories than erythritol (2.4 calories per gram vs. erythritol’s 0.24 calories).
- Digestive Comfort: Erythritol causes fewer digestive problems than xylitol, making it easier to digest for most people.
- Dental Benefits: Both sweeteners help reduce the risk of tooth decay, but erythritol is less likely to cause digestive discomfort.
Erythritol vs. Monk Fruit
Monk fruit, another natural sweetener, is often combined with erythritol in commercial blends.
- Taste: Monk fruit is much sweeter than erythritol. Blending the two creates a balanced flavor in many products.
- Baking Use: Erythritol works better in baking, as monk fruit can alter the flavor of certain recipes.
Erythritol vs. Sugar
Compared to sugar, erythritol offers numerous health benefits.
- Caloric Content: Erythritol contains almost no calories, while sugar has 4 calories per gram.
- Blood Sugar Impact: Sugar raises blood sugar and insulin levels, but erythritol doesn’t affect either, making it a safer option for people with diabetes or those on low-carb diets.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Does erythritol raise blood sugar?
No, erythritol does not raise blood sugar or insulin levels. It has a glycemic index of zero, making it ideal for people with diabetes or those following low-carb diets.
Can erythritol cause digestive issues?
In large quantities, erythritol may cause mild digestive discomfort, such as bloating or gas. However, it is usually well tolerated and causes fewer issues than other sugar alcohols.
Is erythritol safe for everyday use?
Yes, erythritol is safe for daily use. Approved by global food safety authorities, it can be consumed regularly by both adults and children.
How is erythritol produced?
Erythritol is made by fermenting glucose, usually from corn or wheat. After fermentation, the erythritol is purified and crystallized into a sweetener.
Can erythritol be used in baking?
Yes, erythritol is an excellent sugar replacement for baking. You can use it at a 1:1 ratio, but some recipes may need slight modifications since erythritol doesn’t caramelize like sugar.

